
Blog: The Public Transport Workforce in the Artificial Intelligence Era
Today, the world has entered the Fourth Industrial Revolution, driven by the rapid development of advanced digital technologies based on seamless automation and endless connectivity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet-of-Things (IoT), considered to be the most promising technologies, are extensively embedded in numerous physical infrastructure as well as in day-to-day activities. The fast adoption of AI technologies is revolutionising numerous industries from retail to financial services to transportation, re-modelling how people live, work, travel and profoundly impacting the workforce behind the scene.
The Artificial Intelligence Era – Quick Facts
- Worldwide spending on AI systems is estimated to reach US$ 35.8 billion in 2019, an increase of 44% over the amount spent in 2018. (source: International Data Corporation, 2019)
- 61% of surveyed respondents across various industries in the US were implementing AI in their work in 2017. (source: Narrative Science and National Business Research Institute, 2016; survey sample: 196)
Past industrial revolutions deeply transformed jobs. Technologies have repeatedly been developed to take over some of the most monotonous, tiring and demanding tasks to free people’s time, reduce chores’ physical hardness and subsequently improve quality of life. Similarly, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is expected to lead to new work patterns and organisations, new economy markets and lifestyles.

Photo Credit: Timo Elliot on D!gitalist Magazine
What is the scale of this revolution enabled by the rise of autonomous and connected systems?
In very recent years, a prolific number of research papers on AI has been published. Forecasts on the impacts on the workforce vary greatly, yet agree the job displacement will be large scale. In 2013, Frey and Osborne from the University of Oxford evaluated 47% of the US employment are at high risk of computerisation in the next two decades.[2] McKinsey Global Institute reported that between 400 million to 800 million individuals worldwide will see their jobs displaced because of the adoption of automation by 2030.[3] The general public may quickly conclude that AI-powered workplaces will replace human with machines, but many experts predict AI will bring new business opportunities, new processes and skills. Gartner forecasted that 2020 will be the first year whereby AI technologies will create more jobs than they displace, with a net growth of 2 million jobs between 2020 and 2025.[4]
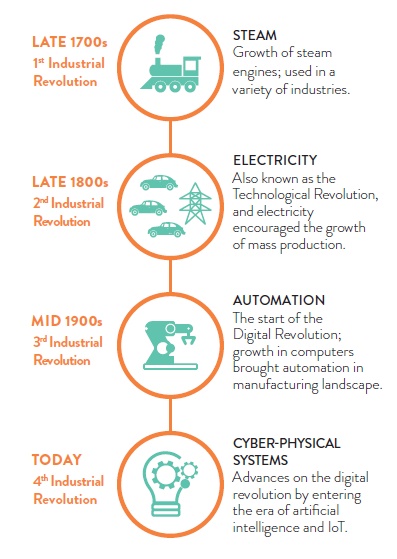
Stages of Industrial Revolution | Source: Adapted from UBS, 2017; Forbes, 2018
The impacts of AI will vary across occupations and industry sectors depending on the nature of the jobs at stake. AI excels in analysing complex data, optimising multiple variables and predicting outcomes. As a consequence, AI is more likely to take over tasks that are repetitive or surrounded by large volumes of data.
AI and the Aging Factor
In countries like Japan, China or Singapore that have a fast-growing aging population, the rapid decline in the labour force is concomitant with a surge in specific needs to take care of the elderly.
AI is seen as a tool to compensate the reduced availability of staff while offering high-quality services. Japan Government aims at building a “Super Smart Society 5.0”, “in which humans and robots and/or artificial intelligence coexist and work to improve quality of life by offering finely differentiated customised services that meet diverse user needs.” (source: The 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan, 2016)
UITP Asia-Pacific Centre for Transport Excellence conducted a year-long study on artificial intelligence in mass public transport with the objectives to raise awareness, draw the current landscape and prepare the industry for the changes to come. In this study, 17 use-cases were collected covering AI applications in public transport customer services, operational and engineering processes, safety and security management. Public transport sector generates large volume of data posing artificial intelligence technologies to find manifold opportunities for growth in all aspects of the industry.
Digital assistants are deployed in some of the highest patronage public transport networks across the globe – London, Tokyo, and Hong Kong among others – to relieve pressure on customer service staff. Chatbots are used to answer customers’ most common queries, allowing employees to deal with less foreseeable passenger needs that require ad-hoc actions. AI can also be implemented as a back-end staff support system as seen at East Japan Railway Company’s call centres. Using natural language processing and pattern recognition, the AI-driven software analyses customers’ queries to call centre agents and automatically displays relevant information on the agents’ screen. Benefits are multiple including a better service to customers with quicker targeted answers, less agents’ work to retrieve information and an increased answer rate.
AI applications are deeply transforming public transport staff workstyle by removing many of the repetitive low-skilled tasks and increasing proficiency in data-driven decision-making. RATPDev developed an AI-based engine that produces automatic origin-destination surveys and monthly reporting, enabling staff to focus on network planning and congestion management matters supported by advanced information. In Hangzhou (China), civil servants adopted a control system powered with image recognition and deep learning technologies that provides real-time traffic recommendations and corrective measures to reduce congestion and optimise responses in case of incidents or disruptions.
None of the current applications reviewed had been deployed with the primary intention to replace staff, instead the workforce was empowered with new and real-time intelligence.AI is currently making significant strides in improving the quality and efficiency of processes as well as tasks undertaken by employees.
In the last decades, automated systems such as driverless metros, self-service ticket machines and journey planners have reduced the number of front-end staff required in public transport networks. The growing adoption of artificial intelligence technologies, in driverless buses, agile dispatching agents and predictive maintenance systems among others, is expected to further transform the public transport workforce. There will be fewer active occupations such as driving or conducting site inspections, and an increased demand for desk-based jobs. Today, there is a need for the public transport industry as a whole, and for organisations individually, to commensurate the impacts of the adoption of AI on their workforce. For instance, the operation of autonomous vehicles (AV) will rely on teams of AV controllers (overseeing fleets of vehicles and acting in case of incidents), AV software programmers, AV maintenance engineers and AV on-board assistants (serving passengers). Mitigating the effects of change in the nature of jobs will require adequate employees’ upskilling and reskilling.
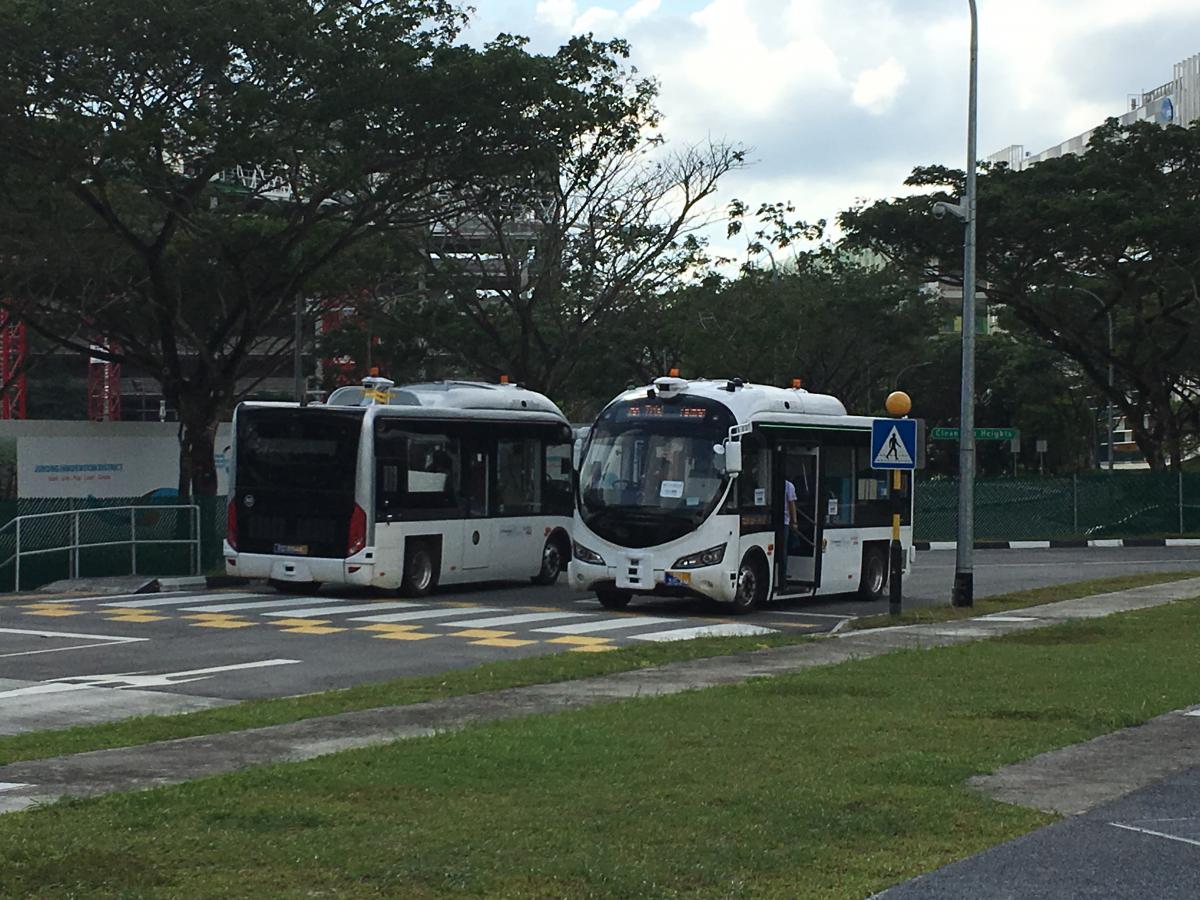

Autonomous shuttles in trial at CETRAN testing facility (Singapore)
AI ≠ Humans: deconstructing some misjudgements
- Human touchpoints are undeniably important in public transport and will continue to be. AI cannot replace human interactions as it cannot develop qualities of empathy, sociability and emotional intelligence.
- AI does not necessary mean less human input. Data preparatory work, such as data labelling and cleaning, is manpower intensive and time consuming, yet critical to develop highly reliable AI systems. It takes approximately 800 human hours to annotate a one-hour clip of driving![5]
- AI excels in handling complex optimisation tasks but is unaware of context. Humans can understand the bigger picture to make strategic and diplomatic decisions.
What are the jobs of tomorrow?
Cross-industry trends indicate the skillsets that will be most needed in AI-powered workplaces:
- IT, data and computer science skills –Teams of digital technology experts developing, supporting and managing AI-based systems will be central to successful businesses of tomorrow.
- Emotional intelligence and care qualities– In highly technology-oriented environments, these most human of people’s qualities will be particularly looked after and a differentiating factor to deliver customer service excellence.
- Creativity and initiative skills – AI can show creativity in the discovery of new patterns in data but is unable to be creative in the general context. Employees will be the driving force for innovation and be essential to deal with unfamiliar or undefined situations.
- Managerial competencies – Occupations that combine AI-savvy, emotional intelligence and strategic thinking skillsets will be even more prominent in the near future. People able to take decisions based on data analytics, understand the multiple subtleties of a situation and comfortable with interpersonal relationships will be key assets to successful organisations.
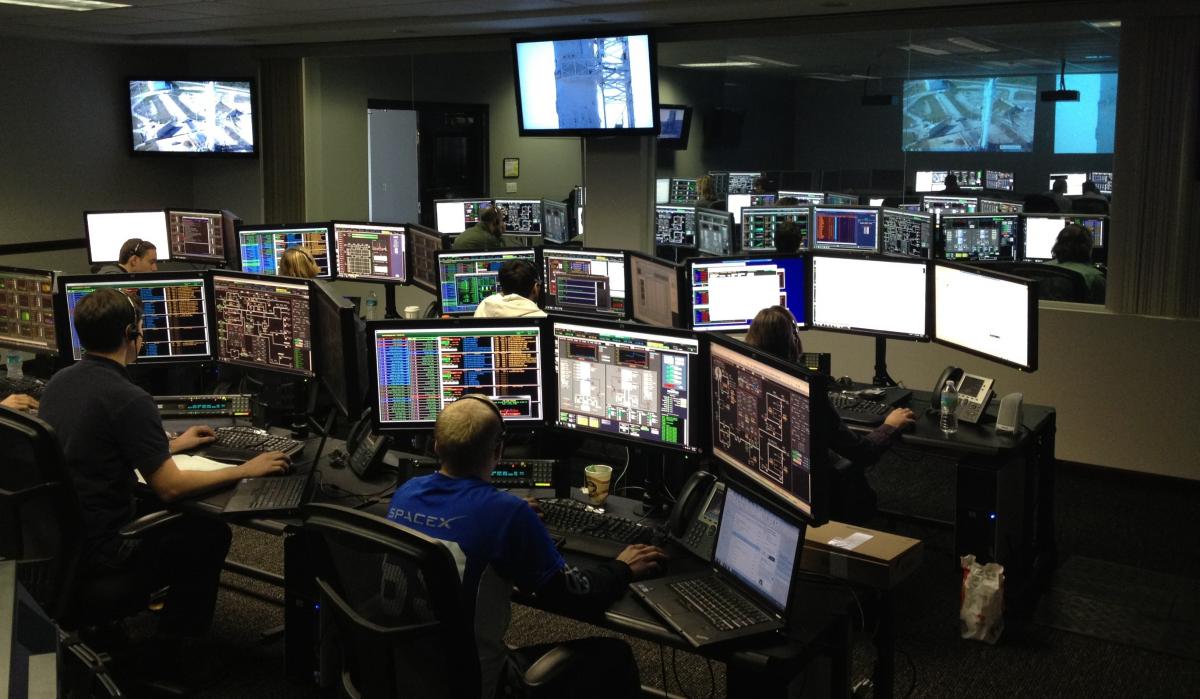

Control rooms are increasingly relying on data analytics system.
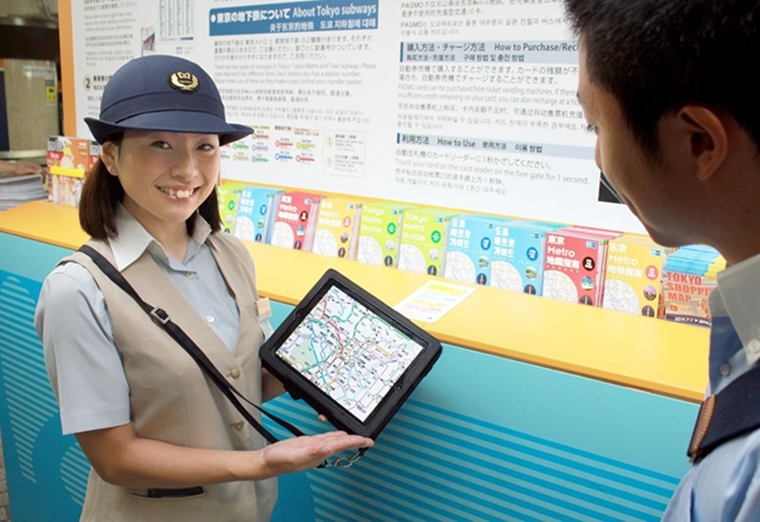

Customer service staff or the human touchpoints of public transport | Photo credit: Tokyo Metro.
Fulfil new jobs with a mix of upgraded skills and fresh expertise.
Training employees and ensuring their skills can upgrade throughout the transformation of the industry will provide a workforce enabled and adapted to new environments embedded with very disruptive technologies such as AI. In addition, hiring new expertise will help organisations undertake change and formulate innovative ideas to transform existing processes. However, the competition to attract data science talents is fierce across industries and public transport will need to position itself as an appealing sector to these experts.
Transform processes to support efficient synergy between staff and AI systems.
Organisations should identify the tasks adapted for artificial intelligence to take over and ensure employees develop AI systems that perform efficiently while being themselves empowered by the technologies. Best processes will be tailored to the organisations’ nature and business, but they will only thrive in data-orientated work environments where the workforce is confident and capable to deal with AI-driven systems.
Adopt an innovation mind-set.
AI is a self-learning technology that needs training and fine-tuning to provide reliable outcomes. To manage preliminary results that can be uncertain, early stages of AI projects often rely on proof of concept development and beta or soft launch. For safety and security reasons, piloting attitudes have not been widespread in the public transport industry. A culture change to accept and support trialling approaches will make employees proactive and rewarded to try, test and sometimes fail, which are the very conditions for innovation. Well managed pilots will be key to ensure failures can happen safely and lessons can be drawn from trials efficiently.
Educate on the risks and benefits of AI and inspire the workforce.
The success of AI-driven transformations will rely on engaging employees from the early stages. On the one hand, manpower should be trained to react and possibly maintain operations in case of technical problems. AI is not a silver bullet, thus organisations should avoid the trap of over-relying on AI. On the other hand, employees are likely to be the ones impacted first and will more eagerly support the change if they feel concerned and stimulated. Future-proof workforce is a key pillar for organisations to thrive in the AI era.
exclusive resources












